Configuring policies in SaaS Guard
SaaS customers can configure their Lakera Guard policies via the Guard platform dashboard. Policies and projects can also be configured via the policies and projects API endpoints.
Note that for enterprise customers, only organization admins have permission to create and edit policies.
View policies
All users can view the policies and their mapping to projects. Navigate to the policies page in Guard to see the list of policies and their high level details.
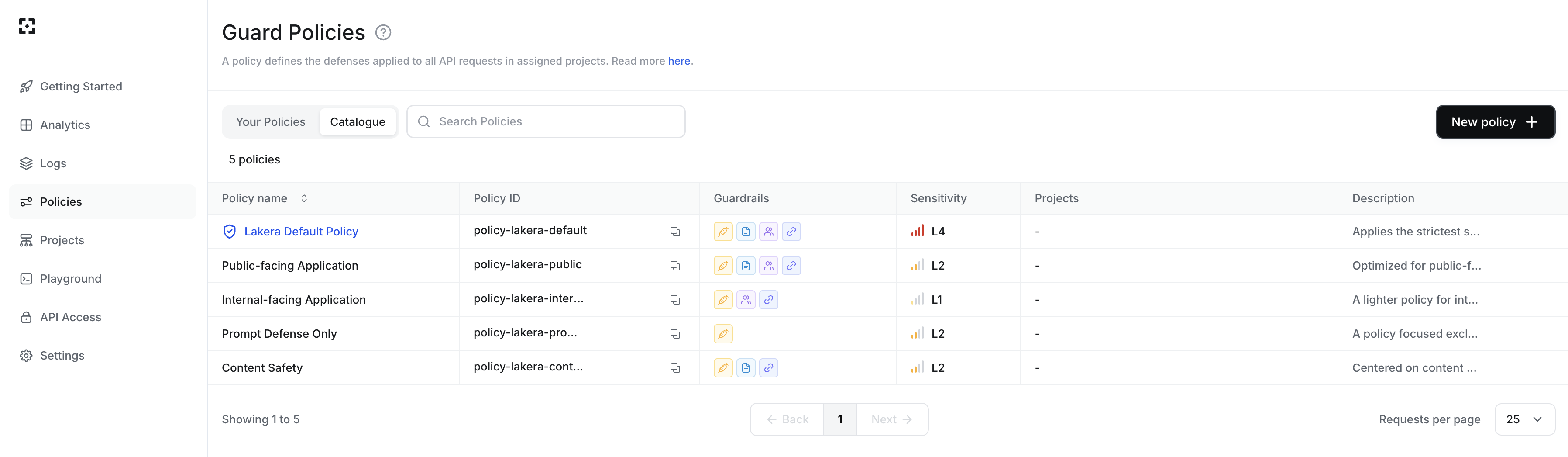
Lakera provides a catalogue of recommended policies by our security experts you can use out of the box. You can also create custom policies using the recommended policies as a starting template, or create from scratch to meet your security requirements.
In the policies table you can select the catalogue or your policies. For each you can see:
- The policy ID, for cross referencing with any logging.
- The guardrails specified in the policy.
- The flagging sensitivity specified in the policy.
- The projects that are mapped to the policy.
- When the policy was last edited, for custom policies.
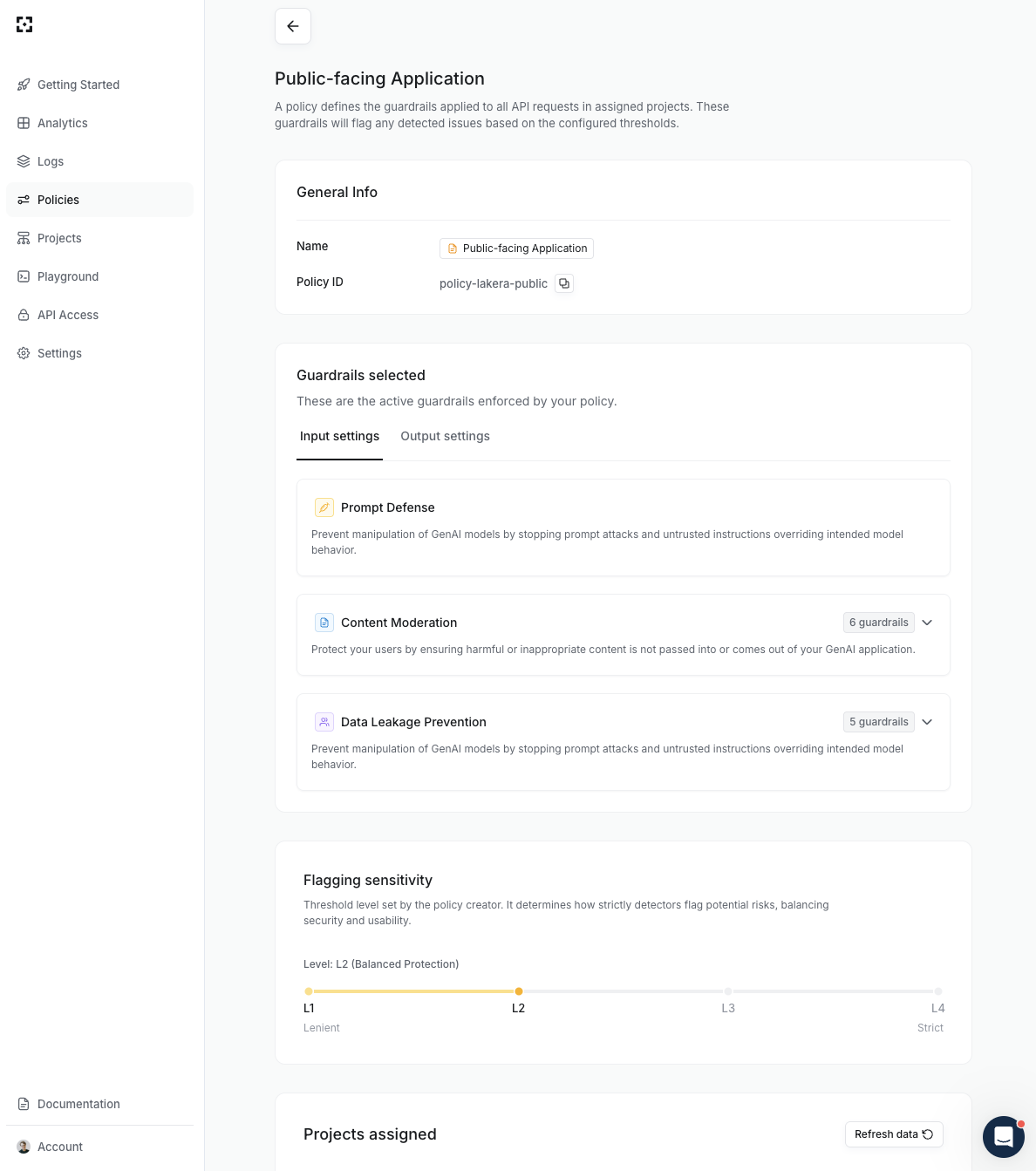
Click on a policy name in the table to view its full details, including the exact list of activated guardrails, any custom detectors, and the flagging sensitivity.
Creating a custom policy
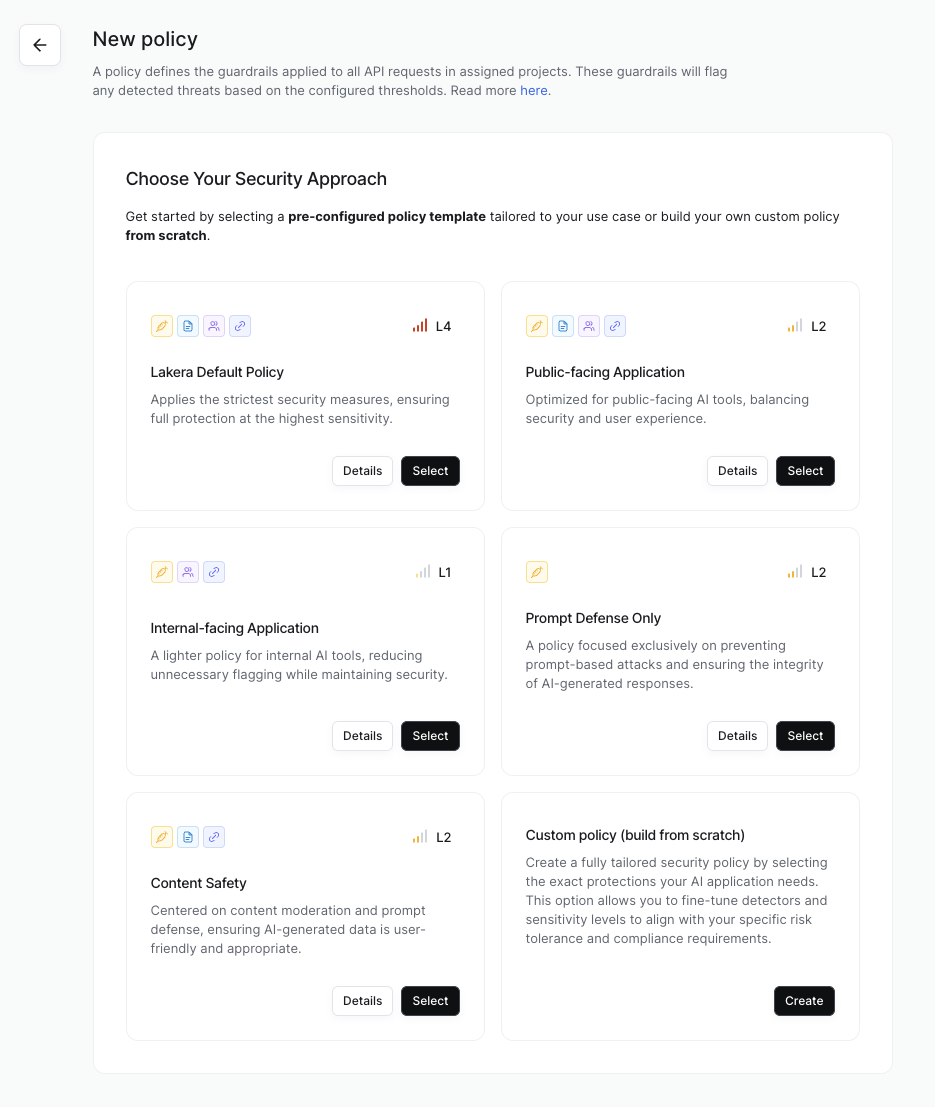
Admins can create new policies by clicking on the New policy button on the policies page.
Choose from a selection of pre-configured policy templates designed by our security experts as a starting point, or build your own custom policy from scratch.
Give your policy a descriptive name. This should help others who see the policy in the platform, API or external logs understand the purpose of the policy and where it’s applicable.
If you’ve chosen a template then the suggested guardrails are listed. The guardrails can be customized, or chosen if building from scratch, through the advanced settings.
Use the slider to set the Flagging sensitivity. This sets the confidence threshold level at which the guardrail detectors will flag the request contents as a threat.
The threshold level can be set from L1, the most lenient, to L4, the most strict. Please see here for more details on flagging sensitivity and threshold levels.
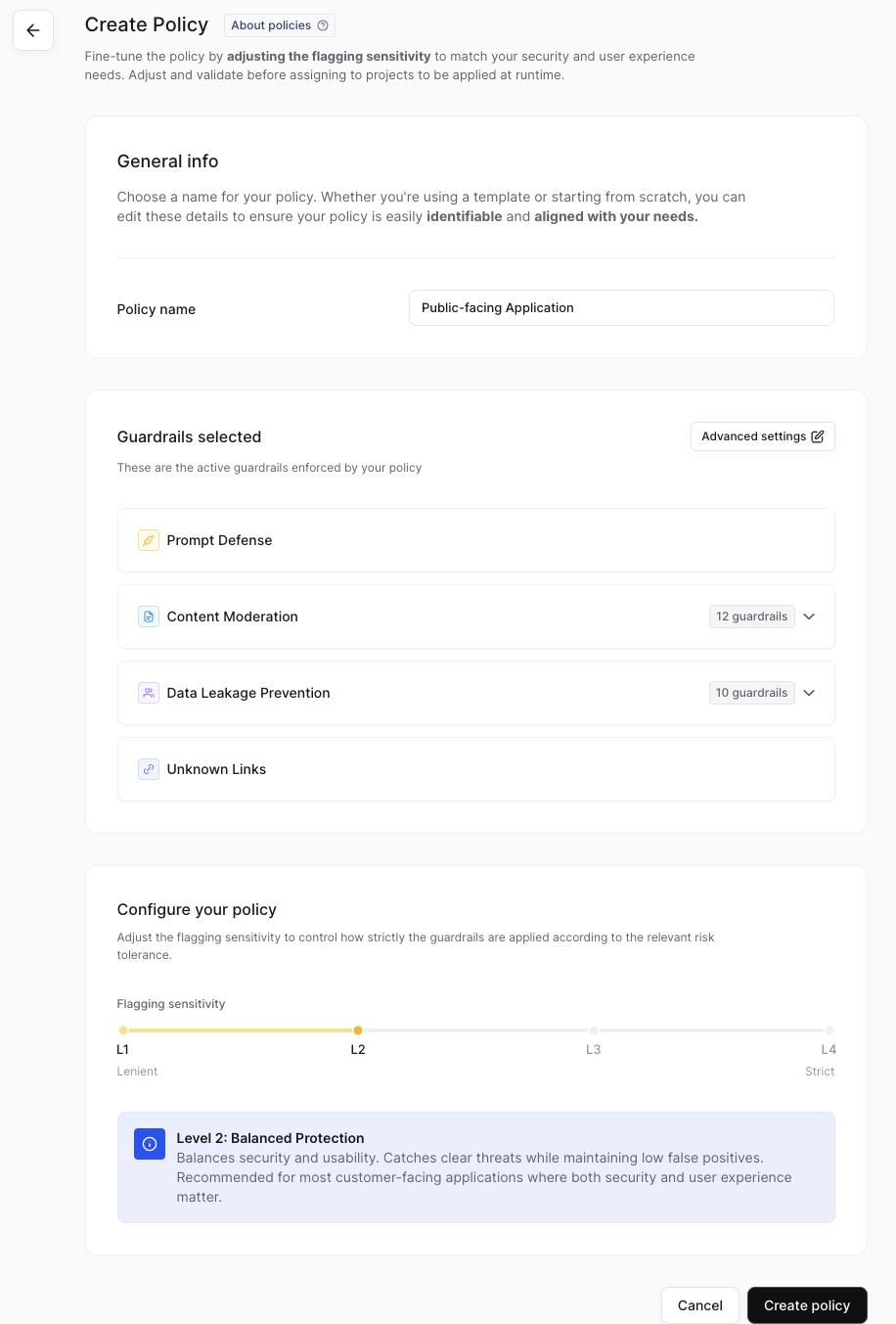
Once you are happy with your guardrail and flagging sensitivity configuration then save the policy.
Assigning policies to projects
For a policy to be used it needs to be assigned to one or more projects.
Once a policy has been created, you can then assign projects to it by selecting and editing those projects in the projects page.
Each project has one policy assigned. The same policy can be assigned to multiple projects.
The projects assigned to a policy will be listed in the view and edit policy pages.
Advanced policy settings
In the advanced policy settings you can customize the guardrails applied and specify whether they should be applied to LLM inputs or outputs, or both.
Select which defense categories should be used for the policy using the toggles. See here for more details on each of them.
In the advanced settings you can also:
- Add custom detectors
- Specify allowed domains for unknown link detection
- Specify allow and deny lists
Custom detectors
In addition to the guardrails developed by Lakera, you can also create custom detectors for the Content Moderation and Data Leakage Prevention categories.
These detectors use regular expressions to flag specific words, strings or text patterns when screening. Note that custom detectors are binary, and they either flag or don’t flag content, independent of the policy flagging sensitivity.
These can be used to add custom defenses, preventing your GenAI talking about unwanted topics or screening for additional types of sensitive data.
For example, you could create a custom PII detector for internal employee IDs, or other forms of national ID. Or you could have a custom content moderation detector that flags any time one of your competitors’ names are mentioned to avoid your GenAI application being tricked into talking about them.
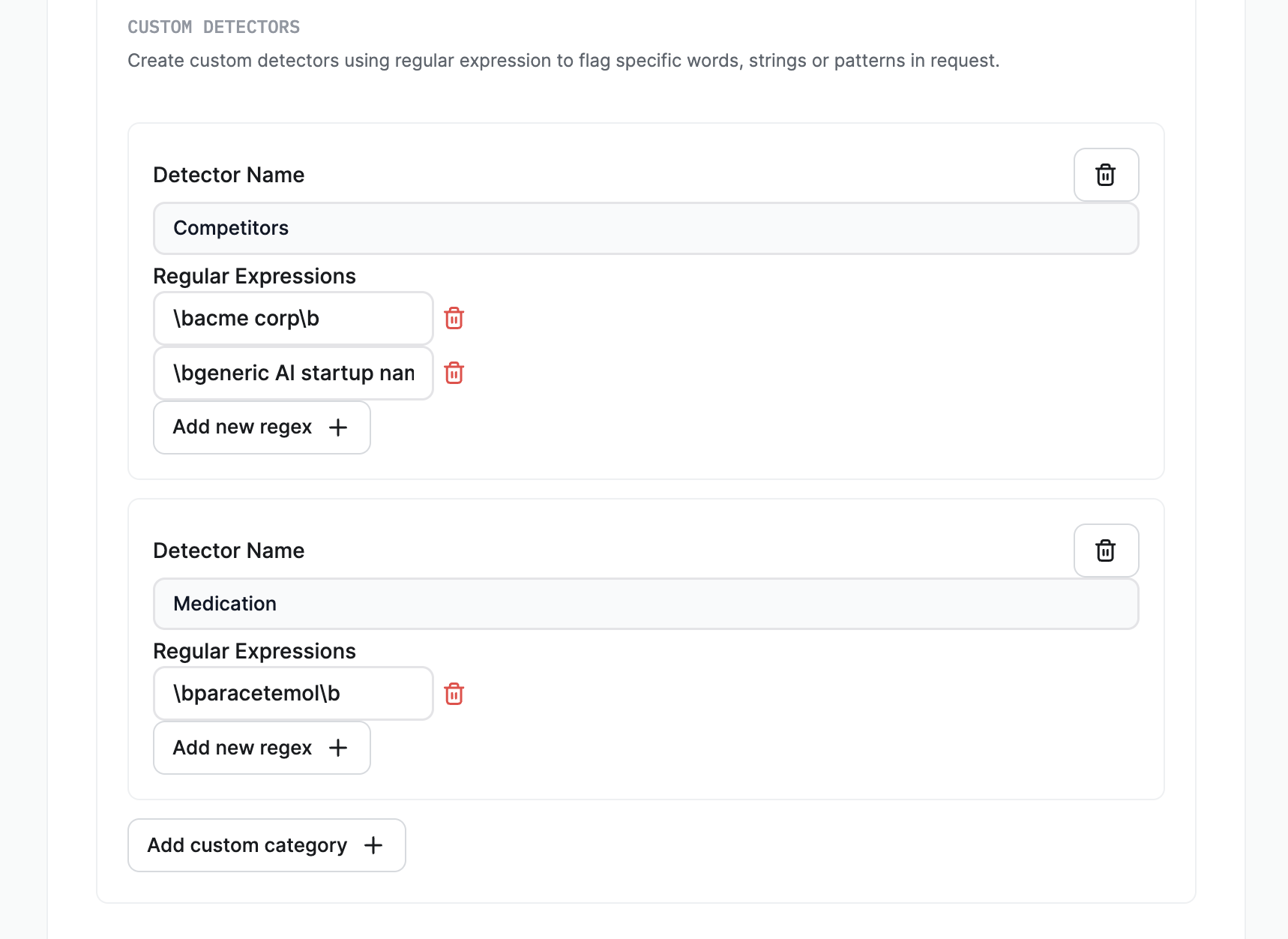
As an example regular expression, you can replace <deny list word> in the below regex with a word or phrase and Guard will flag when it appears in contents, in any casing, and as a standalone word rather than part of another word.
Guard uses Perl-Compatible Regular Expressions (PCRE) syntax. For more information on regular expressions plus guides to creating your own please refer to this useful website, or reach out to support@lakera.ai for help.
Allowed domains for Unknown Links
The Unknown Links detector flags URLs that aren’t in the top one million of the most popular domains. It’s used to prevent malicious links being returned to users by an LLM, e.g. through data poisoning where an indirect prompt injection is hidden in text passed to the LLM that tricks the AI into sharing phishing links.
In the policy, you can specify a custom list of safe domains. The Unknown Links detector won’t flag URLs in the domains added to the allow list. These domains might not be included in the million most popular domains but are safe to appear in LLM interactions. As a result, Guard should not flag them. Usually this will include your own domain.
To add domains to the allowed domains list, click on Advanced editing within the Unknown Links section when you’re editing a policy.
Do not include a subdomain when defining your allowed domains, e.g. platform.lakera.ai, as these are not supported. Only include the domain name and top-level domain.
Allow and Deny Lists
Lakera Guard provides the ability to create custom allow and deny lists to temporarily override model flagging decisions. These lists help you quickly address false positives or false negatives that impact critical workflows while waiting for model improvements.
To access this feature, navigate to the policy edit page and look for the “Allow-list & Deny-list” section.
To add content to your allow or deny list:
- Enable the Allow-list and/or Deny-list toggle
- Enter the exact string of the content to the relevant list
- Click “Add allowed/denied content” to add more content strings to each list
Note that for long term flagging of problematic strings, custom detectors should be used instead of the deny list.
Overriding Lakera Guard can introduce security loopholes. It is recommended to only use allow or deny lists as a temporary measure and report any misclassified prompts to Lakera for robust fixes.
For more detailed information, see the Allow and Deny Lists documentation.
Editing a custom policy
Admins can edit an existing policy either by clicking the edit icon in the actions column of the policies list, or viewing a policy and clicking the Edit policy button.
Note that the preconfigured Lakera catalogue policies, including the Guard Default Policy, cannot be edited.
When editing, you can change the name, the guardrails applied, add or edit custom detectors, and edit allowed domains for unknown link detection.
Once you are happy with your edits then save the policy.
Note that once changes to an existing policy are saved they will take effect within a couple of minutes. This enables you to respond quickly, but means policy changes should be made carefully in order not to accidentally negatively impact your GenAI application or users.
Deleting a custom policy
Admins can delete policies by clicking on the delete icon in the actions column of the policies list.
A policy can only be deleted if there are no projects assigned to it, in order to avoid accidentally affecting your application users. Before deleting, edit each of the assigned projects via the projects page and assign them to another policy first.
Note that the preconfigured Lakera catalogue policies, including the Guard Default Policy, cannot be deleted.
Audit history
All policy creations, edits and deletes are logged to maintain a full audit history. You can see when the policy was last edited in the policy details. If you need a full audit history then reach out to support@lakera.ai.